How To
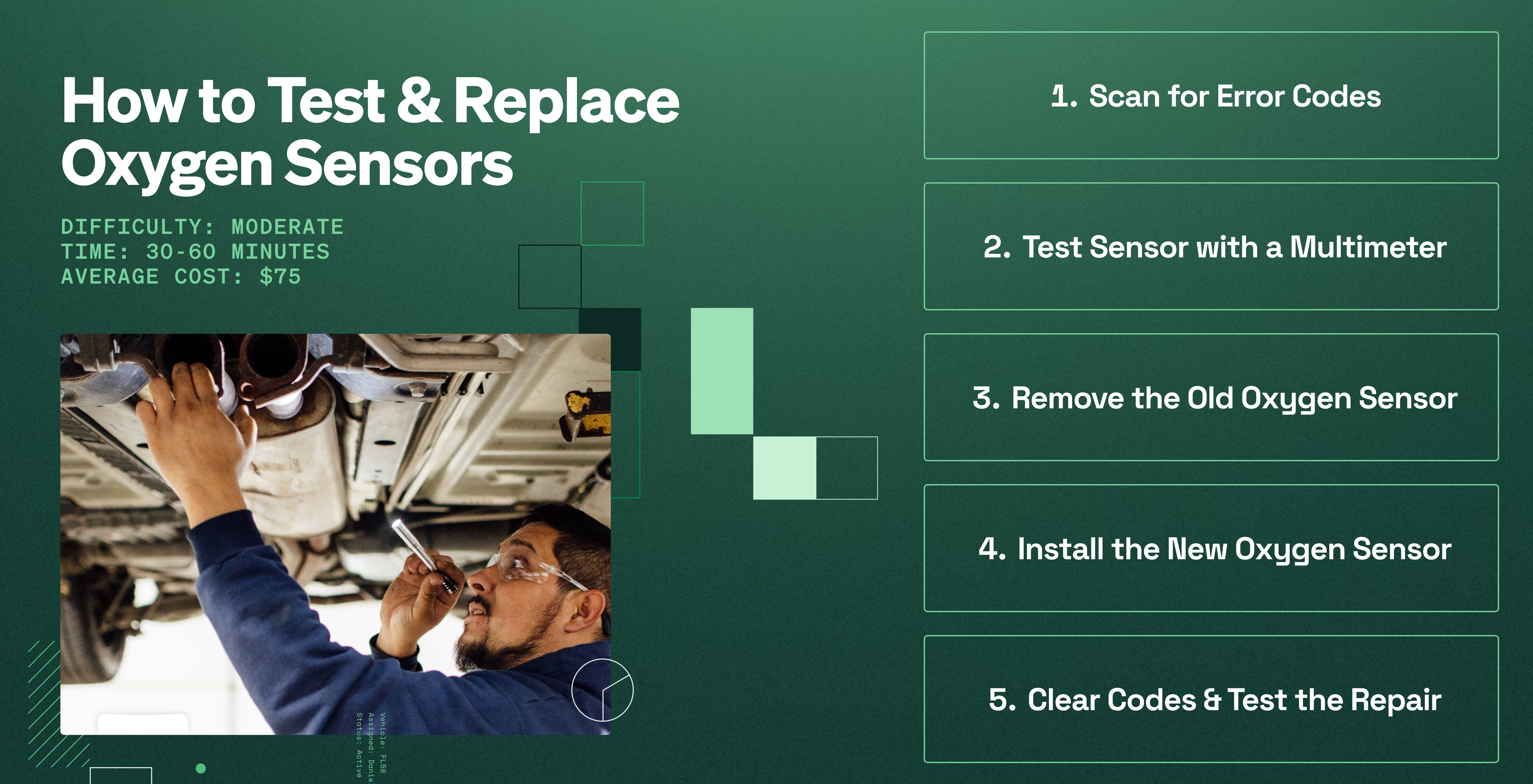
How to Test and Replace Oxygen Sensors: A Step-by-Step Guide
Oxygen (O2) sensors monitor the air-fuel ratio in your engine, helping to optimize performance, fuel efficiency and emissions.

A faulty sensor can cause poor fuel economy, rough idling and a check engine light. Regular testing and timely replacement keep your vehicle running efficiently.
Note
Some vehicles have multiple oxygen sensors located before and after the catalytic converter. Always check your owner’s manual to identify the correct sensor location.
What to Expect
- Time Needed: 30-60 minutes
- Difficulty: Moderate
- Average Cost: $75
Source: 2025 Fleet Benchmark Report
What You’ll Need
OBD-II scanner (to check for codes)
Digital multimeter (for testing sensor voltage)
New oxygen sensor (check owner’s manual for correct type)
Oxygen sensor socket or wrench
Penetrating oil (to loosen rusted sensors)
Anti-seize compound (optional, for installation)
Shop rags & gloves
How to Test and Replace Oxygen Sensors
Step 1: Scan for Error Codes
- Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Look for oxygen sensor-related trouble codes (e.g. P0130, P0135, P0141).
- Identify which sensor is faulty based on the code and sensor location.
Step 2: Test the Oxygen Sensor with a Multimeter
- Locate the oxygen sensor (usually in the exhaust manifold or downstream of the catalytic converter).
- Start the engine and let it warm up to operating temperature.
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage and probe the sensor’s signal wire.
- A good sensor fluctuates between 0.1V and 0.9V. A steady reading or no voltage means the sensor is bad.
Pro-tip
If your vehicle has multiple sensors, compare readings to identify inconsistencies.
Step 3: Remove the Old Oxygen Sensor
- Let the engine cool down completely before starting.
- Spray penetrating oil on the sensor threads and let it soak for a few minutes.
- Use an oxygen sensor socket or wrench to carefully loosen and remove the sensor.
Step 4: Install the New Oxygen Sensor
- Apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the sensor threads (if not pre-coated).
- Thread the new sensor into place by hand, then tighten with a wrench or socket.
- Reconnect the sensor wiring harness securely.
Step 5: Clear Codes & Test the Repair
- Use the OBD-II scanner to clear any stored codes.
- Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes.
- Take a short test drive and monitor for smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency.
Avoid These Common Mistakes
- Skipping the diagnostic scan before replacing the sensor. A check engine light doesn’t always mean a bad oxygen sensor. Scan for codes first to confirm the issue before replacing parts.
- Over-tightening or cross-threading the sensor. Excessive force can damage the threads or sensor, making future replacements difficult. Always tighten to manufacturer specifications.
- Ignoring other potential causes of poor fuel economy. A bad O2 sensor can affect mileage, but vacuum leaks, dirty fuel injectors, or failing catalytic converters can also cause similar issues.
Track service histories across all fleet assets
Fleetio makes it easy to surface fault code alerts, track service history, and set automated maintenance reminders, so every vehicle stays road-ready.
Try Fleetio for FreeFAQs
How often should I replace my oxygen sensor?
Most oxygen sensors last 60,000 to 100,000 miles, but check your owner’s manual for the recommended interval.
What are the symptoms of a failing oxygen sensor?
Common signs include poor fuel economy, rough idling, sluggish acceleration, increased emissions, and a check engine light.
Can I drive with a bad oxygen sensor?
Yes, but a failing sensor reduces fuel efficiency and increases emissions. Over time, it can damage the catalytic converter, leading to expensive repairs.
How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor?
A DIY replacement costs $50 to $150, while a professional repair typically costs $150 to $400, depending on labor and sensor type.
Do all vehicles have the same type of oxygen sensor?
No. Some vehicles use heated or wideband sensors, so always check your owner’s manual or a parts catalog for the correct replacement.



